Some observational studies had found that shift work would increase risks of metabolic disorders, cancers, and cardiovascular diseases by affecting sleep time, circadian rhythm, and other mechanisms, but there was no homogeneous evidence of such an association between shift work and incident dementia, which has important public health implications for the physical and mental health of shift workers.
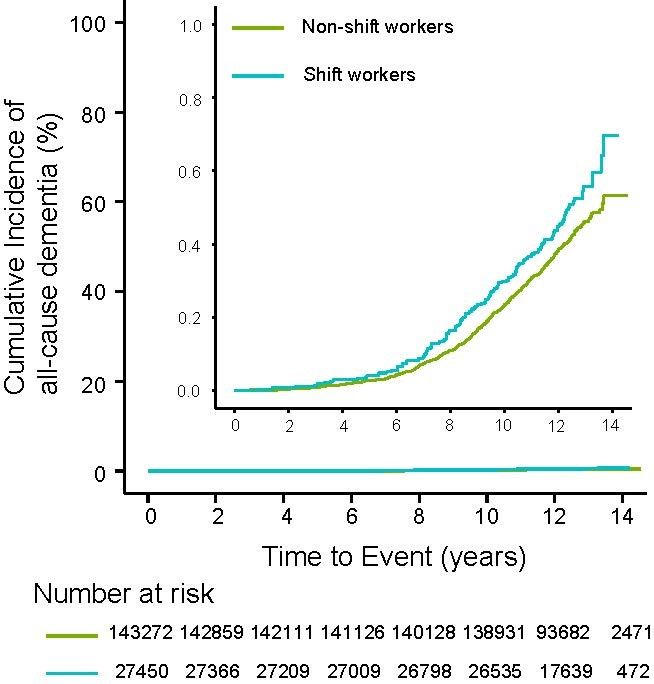
In this prospective cohort study, Prof. Yamei Tang's team at Sun Yat-sen Memorial Hospital included community participants from 2006 to 2010 and selected those who were still employed at enrollment without cognitive impairment or dementia. Shift work status at baseline was self-reported by participants and they were categorized as non-shift workers or shift workers. The primary outcome was all-cause dementia. Over a median follow-up period of 12.4 years, shift workers at baseline had a 30% increased risk of all-cause dementia as compared with non-shift workers. There was no significant interaction between shift work and genetic predisposition to dementia on the primary outcome.
The researchers reveal that shift work was associated with a higher risk of all-cause dementia and this relationship was not altered by the individual genetic predisposition to dementia. This study provides new evidence from a general population and has important public health implications that the occupational health management of shift work should be developed improving the long-term health and quality of life of shift workers. Further prospective cohort studies are needed to investigate the mechanisms by which shift work increases dementia risk, and randomized controlled clinical trials to further investigate the related health management strategy and its effectiveness.
This research was online published in BMC Medicine entitled “Association of shift work with incident dementia: a community-based cohort study” On December 15, 2022. Huanquan Liao, Dong Pan and Zhenhong Deng, Ph.D. candidates from the Department of Neurology, Sun Yat-sen Memorial Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, are the co-first authors of this paper. Prof. Yamei Tang is the sole corresponding author.
The full text is available at: https://bmcmedicine.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12916-022-02667-9
