
Recently, Professor Ming Kuang from the Center of Hepato-Pancreato-Biliary Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University and colleagues published novel mechanisms underlying post-RFA HCC recurrence in internationally renowned journal Hepatology, entitled “Eliminating METTL1-mediated accumulation of PMN-MDSCs prevents HCC recurrence after radiofrequency ablation”. This study opens new avenues to enhance immune surveillance and prevent HCC recurrence after RFA treatment.
Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is an effective curative treatment, which has been recommended for early HCC by guidelines of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD) and European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL). HCC patients benefit from RFA treatment for its safety, minimal invasiveness, and effectiveness. However, similar to surgical resection, the 5-year recurrence rate of RFA treatment could be as high as 70%, remaining a big challenge for HCC management. Insufficient RFA (iRFA) as a result of poorly defined tumor margin or undetected micrometastases provides initial seeds for recurrence, which are subsequently modulated by changes of tumor cell-intrinsic properties and tumor microenvironment. Enormous efforts were taken to prevent tumor recurrence after this therapy but little progress has been made to date. New adjuvant strategies inspired by previously unrevealed mechanisms are urgently needed to improve long-term outcomes of RFA.
By IHC and multiplex immunofluorescence (mIF) staining, they showed that METTL1 expression was enhanced in post-RFA recurrent HCC, accompanied by increased CD11b+CD15+ PMN-MDSCs and decreased CD8+ T cells. Mechanistically, heat-mediated METTL1 upregulation enhanced TGF-β2 translation to form the immunosuppressive environment by induction of MDSC. Liver specific overexpression or knockdown of Mettl1 significantly affected the accumulation of PMN-MDSCs and subsequently affected CD8+ T cell infiltration. Complete RFA (cRFA) successfully eliminated the tumor, while iRFA-treated mice exhibited enhanced tumor growth and metastasis with increased PMN-MDSC accumulation and decreased CD8+ T cells compared to sham surgery. Interrupting METTL1-TGF-β2-PMN-MDSC axis by anti-Ly6G antibody, or knockdown of hepatoma-intrinsic Mettl1 or Tgfb2, or TGF-β signaling blockade significantly mitigated tumor progression induced by iRFA and restored CD8+ T cell population.
This study sheds light on a previously unrevealed role of METTL1 in modulating an immunosuppressive microenvironment, and demonstrated that interrupting METTL1-TGF-β2-PMN-MDSC axis could be a novel therapeutic strategy to restore anti-tumor immunity and prevent HCC recurrence after RFA treatment, meriting further clinical studies.
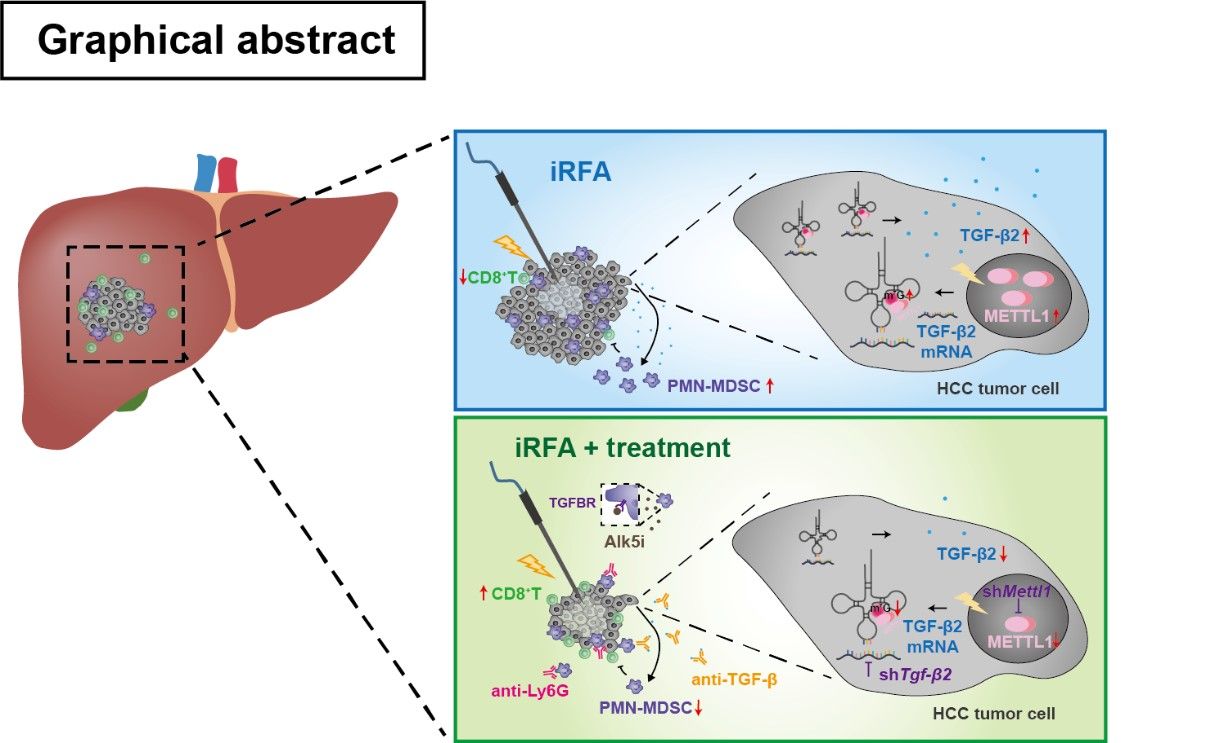
Insufficient RFA promoted METTL1-mediated TGF-β2 translation,which induced PMN-MDSC accumulation and reduced CD8+T cell infiltration. Targeting the METTL1-TGF-β2-MDSC axis significantly ameliorated residual HCC progression.
Xuezhen Zeng, associate research fellow from Prof. Kuang's team, is the first author of this study. Doctoral student Guanrui Liao and postgraduate student Shumin Li are the co-first authors of this study. Prof. Ming Kuang and Ji Wang are corresponding authors.
Link to the paper: https://aasldpubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/hep.32585