Prof. Shi Xiao’s group at Sun Yat-sen University uncovering the roles of phosphatidic acid in the regulation of hypoxia signaling in plants
Source: School of Life Sciences
Edited by: Zheng Longfei, Wang Dongmei
Hypoxia stress is one of the most important environmental factors that affect the growth and yield of plants. The submergence caused by flooding/waterlogging leads to the oxygen tension (hypoxia) of plant cells, thus affects the normal physiological metabolism and the growth of plants. Therefore, it is important to investigate the molecular mechanism of plant perception and signal transduction of hypoxia stress, which is of great scientific and practical significance. To date, the physiological adaptive mechanism of hypoxia response is relatively clear, but little is known about the regulatory mechanism of hypoxia perception and signal transduction in plants.
Previous findings showed that Ethylene Response Factors ERF-VII family proteins anchor at the plasma membrane by interacting with membrane-associated acyl-CoA binding proteins. Under submergence, plants accumulated polyunsaturated acyl-CoA signaling molecules to dynamically respond to hypoxia stress relying on a ubiquitin-like N-terminal protein degradation mechanism, which provide new insights into the role of lipid metabolism or lipid molecules in regulating hypoxic response in plants. Phosphatidic acid (PA) is an essential lipid molecule accumulated in plant responses to hypoxia; however, how PA participates in hypoxia signaling pathway remains unclear.
Recently, Prof. Shi Xiao’ group at Sun Yat-sen University revealed that submergence activates PLDα1 and PLDδ to hydrolyze PE for generating PA, which acts as a signal molecule by binding with MPK3 and MPK6 kinases to enhance their activities. Furthermore, depending on the upstream unknown MAPKKK and MKK5, the MPK3 and MPK6 phosphorylate RAP2.12, a core hypoxic response transcription factor, to regulate its transcriptional activity and hypoxic signaling (Figure 1). Moreover, the accumulation of PA leads to enhanced ROS levels, programmed cell death, and destruction of membrane integrity, which negatively affects plant survival upon recovery post-submergence. Thus, the MPK3 and MPK6 kinases form a regulatory feedback loop with PLDα1 and PLDδ to reduce their protein levels, serving as a protective mechanism for maintaining PA at proper physiological levels under long-term hypoxia conditions.
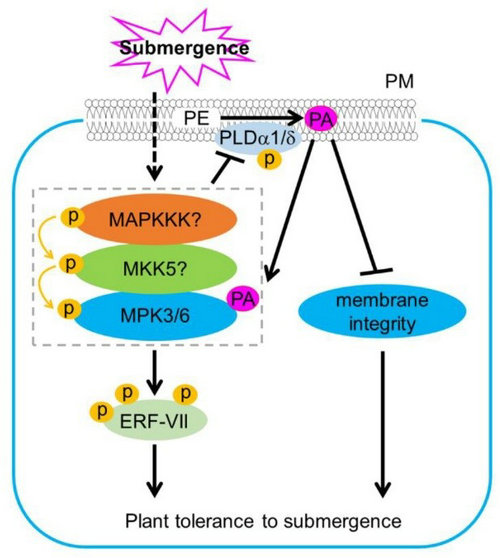
Figure 1. Model of phosphatidic acid regulating hypoxia signal transduction in plants.
The paper entitled “Phosphatidic acid modulates MPK3- and MPK6-mediated hypoxia signaling in Arabidopsis” is recently published in the top journal
The Plant Cell. Dr. Ying Zhou is the first author, and Professor Shi Xiao and Dr. Lijuan Xie are the co-corresponding authors. This work was supported by the funds from the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation.
Link to the paper:
https://academic.oup.com/plcell/advance-article/doi/10.1093/plcell/koab289/6446039?searchresult=1
