Source: School of Life Sciences
Written by: School of Life Sciences
Edited by: Wang Dongmei
Complements are key components of innate immunity that play crucial roles in clearing bacterial pathogens. However, many pathogens are able to evade complement-mediated killing, known as serum resistance. The serum-resistant bacteria always possess antibiotic resistance, whereas the infection by bacteria bearing serum- and antibiotic- resistance is difficult to be eradicated. Even though serum resistance has been documented over 100 years, the strategy for effective management remains poorly understood.
Recently, a team led by Professors Xuanxian Peng, Hui Li, Bo Peng of School of Life Sciences, and Tiantuo Zhang, Zhuanggui Chen of The Third Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University addresses this issue by reprogramming metabolomics. To solve this problem, the team expands their previous concept on reverting antibiotic resistance by reprogramming metabolomics (Cell Metabolism, 2015, 21, 249–261; Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2018, 115, E1578-E1587). They find that the glycine, threonine and serine metabolism is significantly downregulated in serum-resistant bacteria. Exogenous glycine, serine, or threonine reprograms bacterial metabolism to restore their sensitivity to serum as well as to antibiotics. The mechanism involves that glycine, serine or threonine promotes the α-ketoglutarate accumulation that inhibits ATP synthase; Meanwhile, glycine suppresses ATP biosynthesis via purine metabolism. The dual repression of ATP production decreases cAMP/CRP complex that negatively regulates the expression of complement-binding proteins HtrE, NfrA, and YhcD. Moreover, glycine also promotes the production of proton motive force that drives the complement components binding to complement-binding proteins on the bacterial surface. By this approach, serum resistance is reverted. Glycine-triggered reversion of serum resistance is confirmed in human serum, mouse serum, swine serum, fish serum, and shrimp serum. More importantly, this approach is tested in Rag1-/- knockout mouse that lacks T- and B- cell immunity. Thus, this study proposes a novel approach to control bacterial infection in the clinic and the poultry industry.
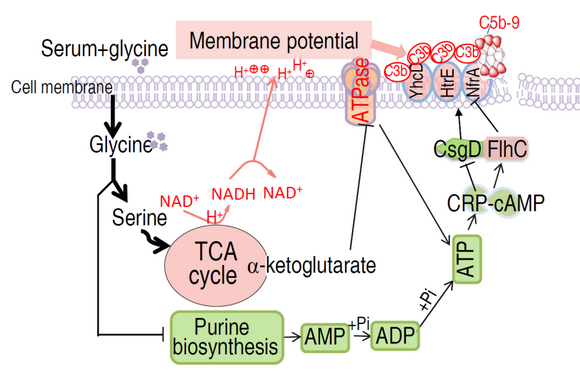
Figure 1. Schematic representation of glycine-triggered reversion of serum resistance
This research not only addresses an issue that has been unsolved for hundreds of years, but also discloses two novel mechanisms: 1) identify a novel regulatory metabolic pathway. 2) metabolite driving metabolic flux overwhelms the effects of gene regulation.
This project is funded by the National Key Research Programs of China (2018YFD0900501/4), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (U1701235, 31822058, 31770045, 41276145). The above-mentioned results were published in
Nature Communications 2019; 10:3325
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-11129-5



